Caring , Celebrating, Developing, Employee Experience, Hiring, High-trust leadership, Inspiring, Leadership & Management, Listening, Managerial Communication, Sharing, Speaking, Thanking
Every employee should take these behaviors to heart whether or not they are people leaders.
I often get asked what it takes to create a great workplace. The short answer: trust.
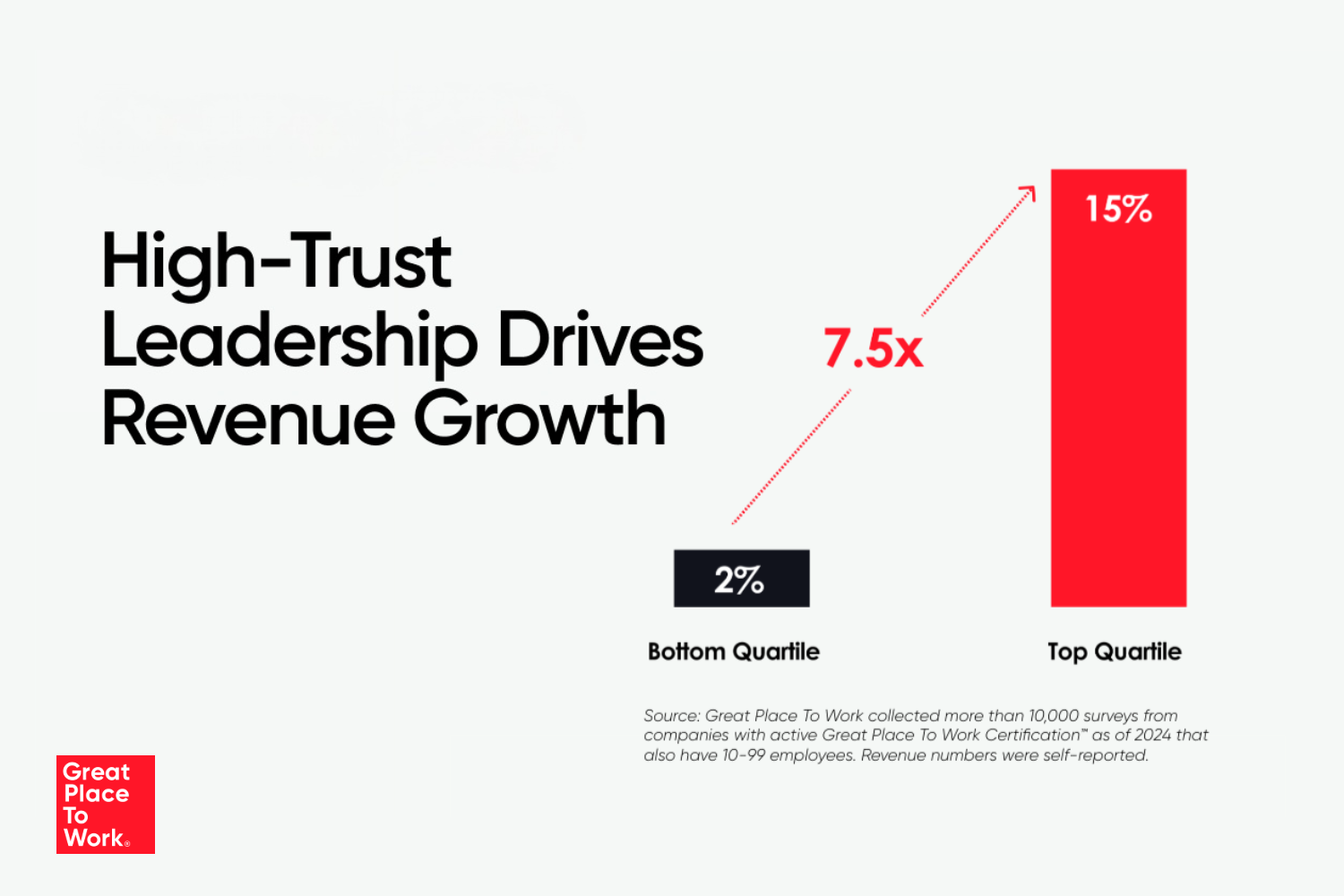
High-trust cultures help employees thrive, which fuels company performance in all areas — from referrals and retention to productivity and revenue. In fact, our research has found that high-trust companies see 8.5x greater revenue per employee than the U.S. public market average. Employees at high-trust workplaces are:
- 28% more likely to adapt quickly to change
- 42% more likely to give extra to get work done
- 45% more likely to say their workplace celebrates innovating and trying new things, regardless of the outcome
Our 30 years of research about company culture has told us that it’s impossible to create a great workplace for all employees without trust — especially as new business challenges emerge, whether it’s remote work, AI, or economic uncertainty. And that’s why our survey that measures employee experience is called the Trust Index™.
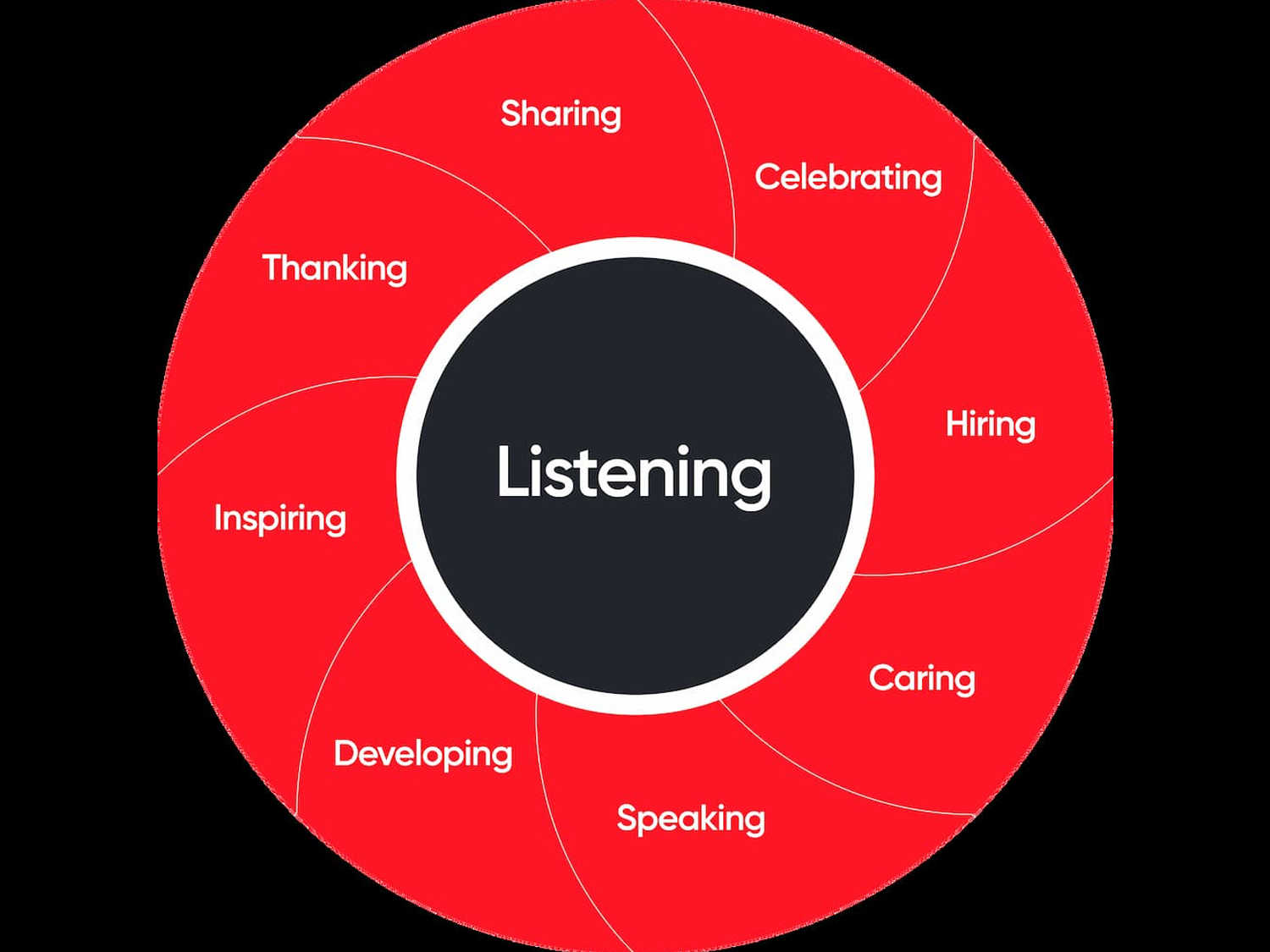
Trust is woven into our daily interactions at work, just as it is outside of work among family and friends. It’s built on many moments — moments that our research has broken down into nine behaviors that can build or break trust. It’s a list I keep on my desk and check-in on how I’m doing as a leader.
Tips and strategies for connecting employee experience to the bottom lineREPORT
How High-Trust Culture Drives Business Success
Every leader should work on and improve these behaviors; if you’re not a people leader, you might be thinking, “What does this have to do with me?”
Leaders affect 70% of the employee experience, but the other 30% comes from our teammates, how we work with others, and the actual work that we’re doing. It takes everyone in an organization to create a great workplace for all.
Here’s where to begin:
1. Listening
This is the most important behavior of all and what I focus on the most. If you’re not a great listener, you can’t model the other behaviors well.
Listening is not just making sure you’ve accurately heard the words coming out of someone’s mouth. It’s also not just waiting for someone to stop talking so you can speak. It is choosing to empty your mind and set aside your opinions while someone else is talking.
True listening requires humility, vulnerability, and empathy.
You may have a lot of opinions, but to be a for-all, inclusive leader, you must put those opinions aside. If you’re having a conversation and you’re not willing to consider other points of view, what’s the point of having the conversation at all? Letting go of your assumptions can be described as a meditative mindset, and that’s what makes a great listener.
How do you know you’re doing it right? You’ll find yourself asking questions because you’re learning something from the person you’re talking to. People will tell you that you’re a great listener because it’s rare to have a conversation with someone who’s deeply listening.
Listening might sound reactive, but it should be proactive. Make yourself available and seek out chances to listen.
Think about who you haven’t heard from lately — and then go ask them questions with a learning mindset. Schedule informal meetings like brown-bag lunches and Q&A sessions. Use surveys and focus groups to regularly elicit employee opinions — and follow up with feedback and action.
Not only might you be surprised by what you learn, but this kind of listening can help your business grow. Financial services firm Synchrony, which has been repeatedly named a Fortune 100 Best Companies to Work For®, saw its stock price double, thanks in part to an immersive leadership program that embraces vulnerability and prioritizes having deeper, more meaningful conversations. The company was able to roll out programs more quickly and effectively just by listening to employees and incorporating their suggestions.
"Listening is not just making sure you’ve accurately heard the words coming out of someone’s mouth. It’s also not just waiting for someone to stop talking so you can speak. It is choosing to empty your mind and set aside your opinions while someone else is talking."
2. Speaking
This is what we do all day. But there are many layers to what might seem like a straight-forward behavior.
Speaking is about clarity, frequency, transparency, and sharing information fully in a variety of ways. That includes regularly sharing company news with employees through all your channels — video, intranet, email, print, etc. Be sure to share that news (both the facts and feelings around it) internally before you do externally.
It’s not just about what you share, but who you share it with. Be mindful of those who haven’t heard a message and need to know what information is being shared.
Speaking is more than what you say and who you say it to, it is how you share information. Inconsistent messaging can quickly erode trust, so communicate thoughtfully and with care, and in easy-to-understand styles. Set up regular meetings to discuss what’s happening, deliver feedback when promised, and personally share news to encourage a culture of transparency as much as possible.
Lastly, speaking is an opportunity to communicate how a person’s job — and how doing their job well — is essential for your organization to achieve its purpose.
Consider your receptionist, for example — a role that is often overlooked. Whenever you speak with them, reiterate, emphasize, and clarify how important their job is. When someone walks in a building or contacts a receptionist on the phone, that’s a connection to the brand. In a few seconds, a caller or visitor either feels cared for, important, and listened to, or they don't.
Speaking is the ability to talk to every warehouse worker, every receptionist, every salesperson, every executive, every teammate in a way that they feel that doing their job is important for the organization to achieve its purpose. And if you’re not sure what someone does, this is your opportunity to build trust by getting to know them.
"Speaking is more than what you say and who you say it to, it is how you share information."
3. Thanking
If you’re listening to people in the way that I described earlier, you’ll learn things about them. That helps you thank your colleagues in ways that are personally meaningful. Acts of gratitude let people know you’re listening in a way that shows they’re important and essential.
Create a culture of appreciation by recognizing good work and extra effort frequently.
Opportunities to do this are endless: Encourage peer recognition, present employee awards, write personal notes, appreciate mistakes as learning opportunities, and recognize employees who demonstrate company values in person and in front of others.
Creating a culture of thanking will positively affect people’s sense of value and willingness to do their best work because they feel seen.
4. Developing
Listening and speaking helps you learn how someone can further develop personally and professionally.
It’s your job to help employees grow as people, not just performers. Nurture their talents and interests through courses (job- and non-job-related), tuition reimbursement, and personalized development plans and training, for example. Connect employees with mentors and inform them of internal job postings.
Try and give feedback in a way that’s measurable, so they know they’re improving, and with a sense of care, so they’re open to what you have to say.
When people know you care — even if they don’t always like hearing where they need to improve — they’ll take it as a gift. Everybody wants to get better. Yes, they know it leads to more money, more compensation, and more responsibility in the company. But, at a base level, they want to know they’re making a difference.
Leaders can even model their own personal development journeys. Share the lessons you’ve learned and mistakes you’ve made — and how you’ve corrected course. This openness shows that no one is perfect and everyone, at all levels, still has room to grow, which fosters psychological safety and trust.
"It’s your job to help employees grow as people, not just performers."
5. Caring
This is the secret weapon. Great work happens when people care. And people care about their work when they experience being cared for. That shows up when you take time to understand and listen to people’s experiences, inside and outside of work.
Support their personal lives by discussing options for flextime and personal leave policies. Help them cope with family and personal crises as they arise, and organize support through sick leave or monetary donations. Encourage work-life balance and remind them to take time off to recharge.
Do you know what makes an employee check an algorithm two or three times, or proofread an email six or seven times? It’s because they care about the purpose of the organization, they care for others, and they feel cared for.
Caring is what unlocks people, and it is key to maximizing a human’s potential.
"Great work happens when people care. And people care about their work when they experience being cared for."
Explore how high-trust cultures outperform the competition in revenue growth, retention, innovation, and stock performance.REPORT
Want to see how trust drives business outcomes?
6. Sharing
Distributing profits, compensation, bonuses, and incentive plans fairly creates an equitable workplace. If you’re building trust for all, every employee needs to share in the company’s success and understanding how their performance relates to compensation.
Equitable and inclusive sharing also shows up in philanthropic activities. If you’re organizing community activities like a cleanup at a local school, or picking up plastic off a beach or park, make sure that everybody has the opportunity to participate.
If you’re doing those things between eight to five, what about the night shift worker? Make sure you’re truly inclusive in terms of sharing opportunities for people, as well as the resources of the organization.
Equity does not equal sameness. A picnic for the day shift doesn’t also have to be a picnic for the night shift. What is the purpose of the picnic? To bring people together, to show them their value, and create opportunities for them to interact in informal ways with their leaders.
So how can you create this same experience for this night shift without recreating the same event?
7. Celebrating
The most important things to celebrate are the values of the organization and how people help the organization achieve its purpose.
It’s important to be specific:
“We want to thank John for the work he did in helping a customer through a sticky problem. We wanted John to do that in seven minutes, but John took 20 minutes because the customer needed it at that time. At our company, we’re willing to do whatever is required to make the customer’s problem our problem, and we’re willing to do what’s required to solve it. I also know that John was late for getting to a soccer practice for his kid. I hope John doesn't have to do that again, but I want to appreciate the fact that he did that for us.”
If you find yourself celebrating, recognizing, and rewarding the same person, communicate to everyone what it takes to be celebrated and recognized so they don’t feel there’s bias or favoritism. They’ll know if they work hard in some measurable way, they too will get celebrated, recognized, and rewarded one day.
"The most important things to celebrate are the values of the organization and how people help the organization achieve its purpose."
8. Inspiring
You don’t have to be a great public speaker to inspire people. You can inspire people with the questions you ask and the way you listen.
You can inspire them by reaffirming the difference your organization makes in the world and why the work is important. Help your workforce understand how their work relates to the company’s higher purpose and business success.
You can do this by telling customer or client stories, sharing the vision of where the company is headed, pointing out behaviors that exemplify company values, reinforcing company values, stressing your company’s contribution to your industry or society, and showing links between employee efforts and achieving your goals.
"You don’t have to be a great public speaker to inspire people. You can inspire people with the questions you ask and the way you listen."
9. Hiring and welcoming
When someone joins your organization, you should make sure that they know you were expecting them — and that you couldn’t wait for them to get here.
You need to make sure that they have a workplace, can access the systems they need to connect with their work and their colleagues, and have the equipment to be successful. Their laptop is ready, their uniform is ready, their steel-toed boots are ready, their safety goggles are ready.
This goes beyond hiring; it’s what we call welcoming. You can email or send new hires a note in the mail before they start, announce them to other employees in advance, take them to lunch their first week, and help them get integrated into your culture.
When a person joins an organization that has shown that they’ve been thinking about them for a few weeks before they started, they will go home and say, “It was a great experience today. They expected me, my name badge was ready. Everybody was kind, and they seemed to know who I was and what I was going to do.” These actions build trust on their first day.
If someone gets to work and those things aren’t true, trust dips a bit. Self-confidence drops. They wonder if you really want them there, or if they’re an afterthought.
And the worst case — they feel like they’re just an employee and not a person who’s important, because if they were important, they would’ve had a much different experience when they arrived.
Whether or not you manage people at work, I encourage you to put this wheel of nine high-trust behaviors in a place where you will see it every day.
Trust takes work and conscious effort. And it’s required to create a great place to work for all.
Become great
Ready to learn more about your employee experience? Benchmark your organization using Certification™ and see how you stack against the very best.
Transform culture into business success
Let our Great Place To Work® Model guide your culture to drive performance. Start your journey with Great Place To Work today.